2017
Shao-Chi Lee, Lin Guo, Huifeng Yue, Hsuan-Hung Liao, Magnus Rueping
Synlett 2017, 28, 2594-2598
Abstract:
We describe Ni-catalyzed decarbonylative silylation, borylation, and amination reactions of amides. Under the optimized conditions, various arylsilanes, arylboronates, and arylamines, which are important building blocks in synthetic chemistry, were prepared with good yields and high stereospecificity. The here-described cross-coupling stands out due to the ready accessibility of substrates, mild reaction conditions, and simple reaction handling allowing a stereoselective product formation.
Osama El‐Sepelgy, Aleksandra Brzozowska, Luis Miguel Azofra, Yoon Kyung Jang, Luigi Cavallo, Magnus Rueping
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14863-14867
Abstract:
Herein a new iron-catalyzed carboetherification of allenols is described. The reaction is not only the first example of the use of an iron cyclopentadienone complex for carbon–heteroatom bond formation but, more importantly, readily available allenic alcohols can be readily transformed into deoxygenated pyranose glycals, which are important building blocks for the synthesis of bioactive molecules and natural products. Mild reaction conditions, good functional-group tolerance, and low catalyst loadings of an air-stable inexpensive iron complex are characteristics of this new transformation. Computational studies support a reaction mechanism in which the iron cyclopentadienone complex plays a dual role. While the catalytically active 16e iron species coordinates to the allene, the non-innocent cyclopentadienone ligand acts as a proton shuttle by initial hydrogen abstraction from the alcohol and by facilitating protonation and deprotonation events in the isomerization and demetalation steps. Furthermore, the unexpected formation of the 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran as opposed to the previously observed 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran could be explained through molecular orbital analysis of the iron vinylidene intermediate, which demonstrated that formation of the enol product is more favorable. Thus, the results of this combined computational and experimental study will guide explorations in the design of further new reactions promoted by metal–ligand cooperative catalysis with iron cyclopentadienone tricarbonyl complexes.
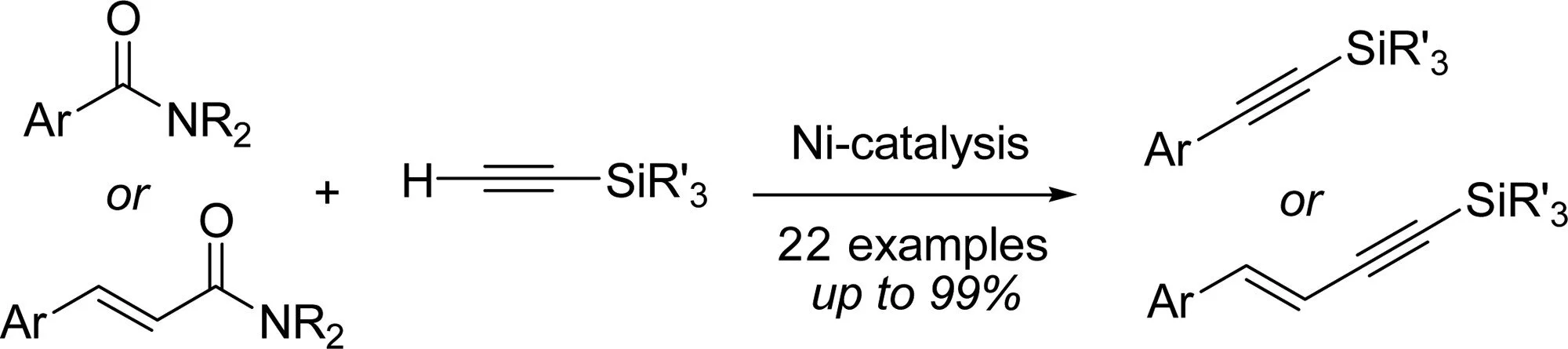
Dr. Xiangqian Liu, Huifeng Yue, Jiaqi Jia, Lin Guo, Magnus Rueping
Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 11771-11775
Abstract:
Herein we describe an efficient extrusion recombination fragment coupling of amides through a nickel-catalyzed C−N activation. The new protocol allows the amide to amidine interconversion without reducing reagents, the use of esters, activated amines or an additional amine source. The high chemoselectivity of our amidine synthesis protocol, paired with the reduction of amide to amine, offers opportunities to access more complex substrates with multiple amino groups. Compared to traditional amidine synthesis procedures, the new protocol distinguishes itself by its high atom efficiency, the use of readily available amides, and low amounts of an inexpensive nickel(II) catalyst and, thus, the new fragment coupling strategy provides a viable alternative for the synthesis of amidines.
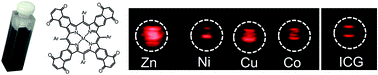
13. Quinone-fused porphyrins as contrast agents for photoacoustic imaging
Srinivas Banala, Stanley Fokong, Christian Brand, Chrysafis Andreou, Bernhard Kräutler, Magnus Rueping and Fabian Kiessling
Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6176-6181
Abstract:
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is an emerging non-invasive diagnostic modality with many potential clinical applications in oncology, rheumatology and the cardiovascular field. For this purpose, there is a high demand for exogenous contrast agents with high absorption coefficients in the optical window for tissue imaging, i.e. the near infrared (NIR) range between 680 and 950 nm. We herein report the photoacoustic properties of quinone-fused porphyrins inserted with different transition metals as new highly promising candidates. These dyes exhibit intense NIR absorption, a lack of fluorescence emission, and PA sensitivity in concentrations below 3 nmol mL−1. In this context, the highest PA signal was obtained with a Zn(II) inserted dye. Furthermore, this dye was stable in blood serum and free thiol solution and exhibited negligible cell toxicity. Additionally, the Zn(II) probe could be detected with an up to 3.2 fold higher PA intensity compared to the clinically most commonly used PA agent, ICG. Thus, further exploration of the ‘quinone-fusing’ approach to other chromophores may be an efficient way to generate highly potent PA agents that do not fluoresce and shift their absorption into the NIR range.
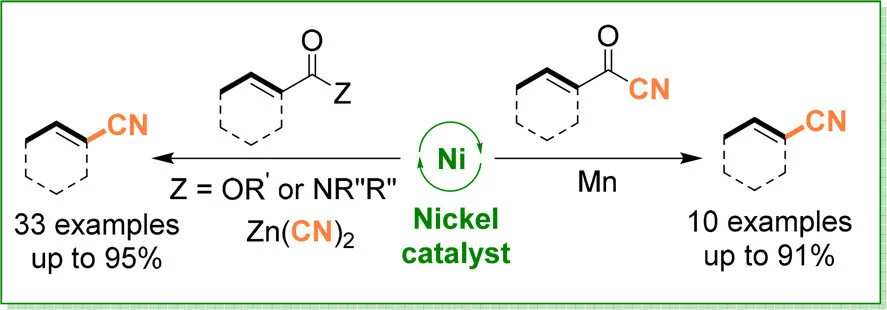
Adisak Chatupheeraphat, Hsuan-Hung Liao, Shao-Chi Lee, Magnus Rueping
Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4255-4258
Abstract:
Herein we describe the first nickel-catalyzed decarbonylative cyanation protocol which allows the transfer of a series of readily available aryl and heteroaryl esters as well as amides to the corresponding nitriles. This protocol provides a new possibility to cleave carboxylic esters and amides while forming a C–CN bond. The newly developed protocols successfully suppress the undesired acyl cyanide formation, nitrile product decomposition, and catalyst poisoning processes. In order to prevent byproduct formation, a nickel(II)-catalyzed extrusion recombination fragment coupling strategy allows direct access to aryl, heteroaryl, and cinnamonitriles starting from the corresponding acyl cyanides. The new methods are characterized by high efficiency, chemoselectivity, and excellent functional group tolerance, providing a practical and versatile approach to a wide range of aryl and heteroaryl nitriles.
Chengming Wang, Ai Wang, Magnus Rueping
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9935-9938
Abstract:
We report a new manganese-catalyzed C−H functionalization method. This redox-neutral process provides alkenylated indoles as well as pyrroloindolones in high yields with excellent regio- and stereoselectivity. Mechanistic studies suggest the formation of a cyclometalated manganese complex that reacts with an allene via a manganacycle to provide the alkenylated product. The use of trisubstituted allenes resulted in an unexpected heteroaryl shift via a C−H functionalization/C−N bond cleavage/cyclization sequence to provide a new synthetic approach to valuable pyrroloindolone scaffolds.
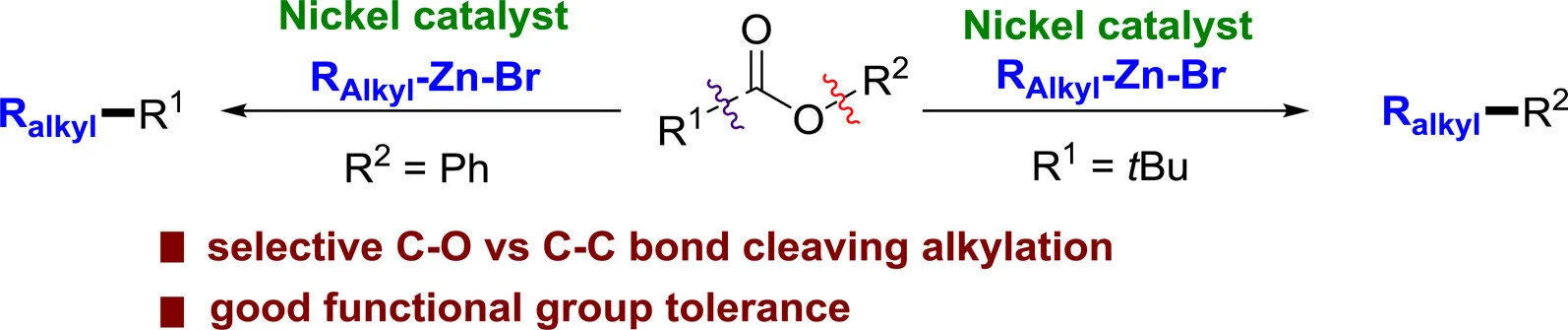
Xiangqian Liu, Jiaqi Jia, Magnus Rueping
ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4491-4496
Abstract:
We have developed two nickel-catalyzed aryl–alkyl cross-coupling reactions using esters as electrophilic coupling partners. The right choice of ester and catalyst allows controlling the selective oxidative addition of nickel to an acyl C–O or an aryl C–O bond, thus allowing the selective introduction of alkyl groups to the carboxylic acid component via decarbonylative bond cleavage or phenol component via C–O bond cleavage. The protocols are characterized by their efficiency and functional group tolerance with regard to both coupling partners. The newly developed aryl–alkyl cross-coupling reactions described herein may not only become a good alternative to the standard halide-based cross-couplings but also lead to late-stage synthetic strategies and unconventional utilization of esters and their carboxylic acid and phenol precursors in synthetic chemistry. Moreover, the synthetic utility has been demonstrated by the application of the method to the synthesis of naproxen analogues. Although further mechanistic and computational studies need to be part of our future research, we believe that the direct replacement, in particular, the first example of a direct exchange of the ester moiety by a long chain functionalized alkyl chain, will be of use in retrosynthesis, late-stage functionalizations, and synthesis in general.
Watchara Srimontree, Adisak Chatupheeraphat, Hsuan-Hung Liao, Magnus Rueping
Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 3091-3094
Abstract:
A new and selective cross-coupling reaction of amides with terminal alkynes as coupling partners has been developed. The direct, one-step transformation of an aryl or alkenlyl amide to the corresponding alkyne was previously not known and is, with conventional methods, difficult to achieve. Thus, the newly developed methodology enables a facile route for C(sp2)–C(sp) bond formation in a straightforward fashion by successful suppression of the undesired homocoupling process. Various terminal silyl alkynes and a wide range of aromatic amides bearing various substituents are tolerated in this process, which afforded products in good to excellent yields. The utility of this newly developed protocol has been demonstrated in the synthesis of enynes as well as large-scale synthesis of silylated alkynes. Given the simplicity and generality of the protocol, it is anticipated that it should find application in synthesis, retrosynthesis, and late-stage modification.
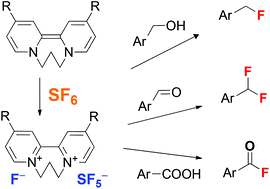
Magnus Rueping, Pavlo Nikolaienko, Yury Lebedev, Alina Adamsc
Green Chem., 2017, 19, 2571-2575
Abstract:
We report the use of organic electron donors for the activation of the greenhouse gas, sulphur hexafluoride. Bipyridine-based organic electron donors were found to react fast and selectively with SF6 at ambient temperature in non-polar aprotic solvents within minutes to yield solid ion pairs consisting of donor dications [D2+] and fluoride [F−] and [SF5−] anions. The presence of the SF5− anion was confirmed by NMR- and IR-spectroscopy analysis. The salts can be isolated and also be applied as fluorinating reagents. This was demonstrated by the deoxofluorination of alcohols, aldehydes as well as carboxylic acids. Thus, SF6 is a readily available and stable precursor for the otherwise more difficult to handle deoxofluorinating reagent, sulphur tetrafluoride. Given the simplicity of the procedure it can be used for both, the decomposition of one of the most potent greenhouse gases and at the same time the generation of a powerful fluorinating reagent. Further applications of this metal-free activation of SF6 as well as demonstration to reuse and recycle the electron donors are currently part of our further research.
Osama El‐Sepelgy, Aleksandra Brzozowska, Magnus Rueping
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1664-1668
Abstract:
A noble metal-free cascade process for the conversion of prochiral ketones into highly enantioenriched acetates has been developed. The simple and inexpensive iron and lipase multi catalytic system operates via a hydrogenation/dynamic kinetic resolution cascade. It is important to note that the iron catalyst is not only able to reduce the ketone in the presence of the enzyme but additionally catalyzes the dehydrogenation of the alcohol under hydrogen atmosphere. Thus, a wide range of ketones, including benzylic, aliphatic, heteroaromatic, and aromatic, as well as diketones, were reductively acylated and the corresponding products isolated with very high yields and enantioselectivities. The newly developed protocol distinguishes itself through the absence of precious metals or expensive chiral ligands, its operational simplicity, mild reaction conditions, and broad substrate scope. The good compatibility of the readily available and inexpensive iron hydrogenation/racemization catalyst with the biocatalytic resolution calls for further application of this dual catalytic method.
David C. Fabry, Yee Ann Ho, Ralf Zapf, Wolfgang Tremel, Martin Panthöfer, Magnus Rueping and Thomas H. Rehm
Green Chem., 2017, 19, 1911-1918
Abstract:
For the first time the falling film microreactor technology was successfully applied to a photochemically catalysed reaction with TiO2 as an immobilized photocatalyst in the microchannels of a continuous-flow reactor. A wide variety of arenediazonium salts were used as the starting material for blue light mediated C–H arylation of heteroarenes in continuous-flow mode. Furan, thiophene and pyridine as well as furfural were converted into the desired products with good to excellent yields up to 99%. A long-term run over 180 min was successfully performed as well in order to demonstrate the catalyst performance. Detailed XRD, SEM and EDX analyses of the catalyst material before and after calcination and its use in the microreactor, respectively, proved the excellent stability and usability of TiO2 as an immobilized photocatalyst in a continuous-flow microreactor. The transfer of the C–H arylation of heteroarenes from batch mode to continuous-flow revealed a boost in the specific reactor performance up to a factor of 6000. This strong increase can be attributed to the improved irradiation and substrate–catalyst–light interaction on the microstructured surface of the continuous-flow reactor. These results clearly show the major advantages for photochemistry when performed in a microstructured environment.
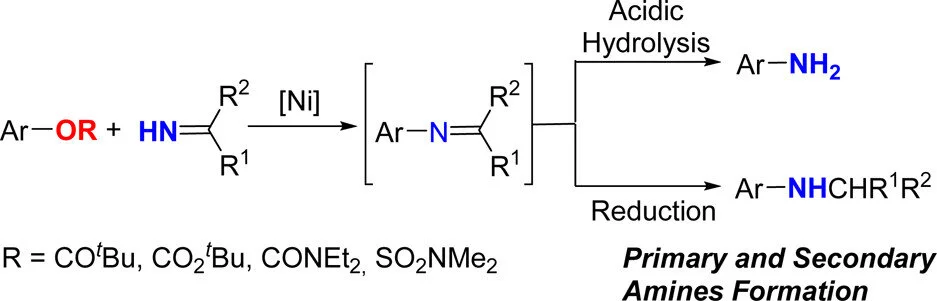
5. Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Primary Aryl and Heteroaryl Amines via C–O Bond Cleavage
Huifeng Yue, Lin Guo, Xiangqian Liu, Magnus Rueping
Org. Lett. 2017,19, 1788-1791
Abstract:
Herein we describe a Ni-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of aryl esters with benzophenone imines. The protocol constitutes the first general strategy for the preparation of primary aryl amines via Ni-catalyzed inert C–O bond cleavage. Considering the substrate scope of this protocol, the method provides a new and efficient route to aryl amines from readily available aryl esters. The protocol shows good chemoselectivity, and functional groups including fluoride, ether, or nitril groups previously used in cross-couplings remain intact. Since aryl and heteroaryl amines are highly valuable products for many different applications this new amination protocol will be of value and may become a good alternative to aryl halides amination reactions.
Huifeng Yue, Lin Guo, Hsuan‐Hung Liao, Yunfei Cai, Chen Zhu , Magnus Rueping
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4282-4285
Abstract:
Herein we describe the first catalytic decarbonylative amination protocol which allows, for the first time, the transfer of a series of readily available aryl and heteroaryl esters, and even amides, to the corresponding amines. In contrast to classical multistep rearrangement procedures, the method relies on the use of either [Ni(cod)2]/dcype catalytic system or the use of a nickel(II) salt to directly provide the desired amines. Considering the substrate scope of this protocol, the method provides a new and efficient route to aryl amines from readily available esters. The protocol shows good chemoselectivity, and functional groups including C−OMe, C−SMe, C−F, and CN moieties, previously used in cross-couplings, remain intact. Since aryl and heteroaryl amines are highly valuable products for many different applications this new ester to amine interconversion will be of value and may become a good alternative to aryl halides amination reactions.
Huifeng Yue, Lin Guo, Shao‐Chi Lee, Xiangqian Liu, Magnus Rueping
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3972-3976
Abstract:
An efficient protocol for the decarbonylative reduction of a wide range of readily available aryl and heteroaryl esters and amides is described. This versatile method for the removal of ester and amide functional groups from organic molecules relies on the use of an inexpensive and air-stable Ni(OAc)2⋅4 H2O catalyst and a commercially available hydrosilane. In contrast to previously reported hydrosilylation reactions, which result in the formation of alcohols, aldehydes, ethers, or amines, the new protocol allows the full removal of an ester or amide group and could be useful for the late-stage modification of compounds or reaction sequences in which carboxylic acid groups are initially used as directing groups for ortho lithiation or C−H functionalization. Importantly, various functional groups often used as electrophiles in nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling or reduction are compatible with the reaction conditions used. Furthermore, the new method can be scaled up readily and applied as a key step in synthetic transformations in which a carboxylic acid group is used as a removable directing group.
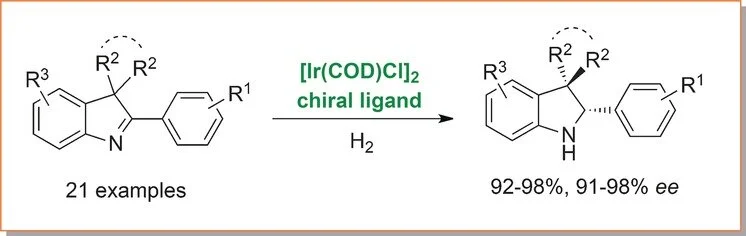
Ruediger Borrmann, Nils Knop, Magnus Rueping
Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 798-801
Abstract:
We report a highly enantioselective synthesis of valuable disubstituted and spirocyclic 2-aryl-indoline scaffolds, which represent an important class of biologically active molecules and privileged structures in medicinal chemistry. The hydrogenation protocol shows good functional-group compatibility and a variety of substituents are tolerated. It is worth noting that halides including fluorine, chlorine, and bromine can also be applied and no dehalogenation has been observed due to the mild reaction conditions and low catalyst loading (1 mol %) applied. In addition, the protocol is amenable to upscaling and the products are obtained in good yields and acceptable enantioselectivities (21 examples, 92–98 % yield, 91–98 % ee). Given that no protecting groups are needed and low catalyst loadings together with molecular hydrogen can be applied under mild and operationally convenient reaction conditions, this protocol should be of practical value.
1. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Cyclic Imines and Enamines: Access to 1,5-Benzodiazepine Pharmacophores
Ruediger Borrmann, Rene M. Koenigs, Jochen Zoller, Magnus Rueping
Synthesis 2017, 49, 310-318
Abstract:
A new strategy towards the pharmacologically relevant class of dihydro-1,5-benzodiazepines was developed by applying a rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation. The approach represents an efficient protocol providing access to the optically active products in excellent yields (up to 99%) and with high enantioselectivities (up to 92% ee). The versatility of the methodology was demonstrated by a broad substrate scope including alkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl substituents as well as halides. Furthermore, investigations regarding the reaction mechanism were performed and unraveled a preferred reaction of the tautomeric enamine in the rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation.